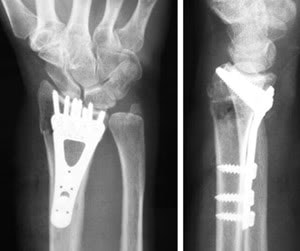
Distal Radius (Wrist) Fracture
What is a Distal Radius (Wrist) Fracture?
Common Treatments may include:
Helpful Links for More Information
- The radius is the larger of the two long forearm bones that connects the elbow to the wrist.
- A distal radius fracture occurs when the end of the bone, closest to the wrist, breaks.
- This often happens when a person falls onto an outstretched hand.
- The distal radius fracture is the most commonly occurring fracture in the arm.
- Common Symptoms
- Pain, tenderness, bruising and swelling following an injury in the wrist and hand, particularly a fall onto an outstretched hand.
- Stiffness or inability to move the wrist.
- In a more severe fracture, the wrist may have an unusual bump or be positioned at an odd angle.
- If the fracture is complex or offset, a surgery may be need to position the bone in proper alignment while the fracture heals.
Common Treatments may include:
- Depending upon the severity of the fracture or the degree of stability of the fracture, use of a wrist brace, splint or orthotic or cast at all times until the bone has healed (approximately 5-6 weeks following injury)
- If the fractured bones are so offset that they can not be held in stable alignment with a cast, surgery may be required to stabilize the fracture.
- Following the immobilization period, treatment may include:
- Regaining mobility of the joints that had to be immobilized during the healing phase.
- Gradually regaining strength in the hand, wrist and arm.
- Use of Heat and cold
- Use cold packs for acute pain or swelling.
- Use heat packs to control more chronic pain or relax the muscles.
- Alternating heat and cold (a contrast bath routine) can be particularly helpful following a wrist fracture to reduce swelling and improve flexibility of the joints.
- Wearing compression sleeves or Isotoner gloves at night may help control swelling and provide a comforting, neutral warmth.
- Modalities such as ultrasound and electrical stimulation may reduce inflammation and pain.
- Scar management techniques if surgery was required.
- Techniques to reduce swelling such as using a compression glove or sleeve, electrical stimulation, use of cold packs, elevation of the arm.
Helpful Links for More Information
- American Society of Hand Therapists (ASHT) - PDF Educational Handout
- American Society for Surgery of the Hand (ASSH) -Website Information.
- American Society for Surgery of the Hand (ASSH) - 3 minute informational video.
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) - Website Information
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) - 3 minute informational video on bone healing and cast care.